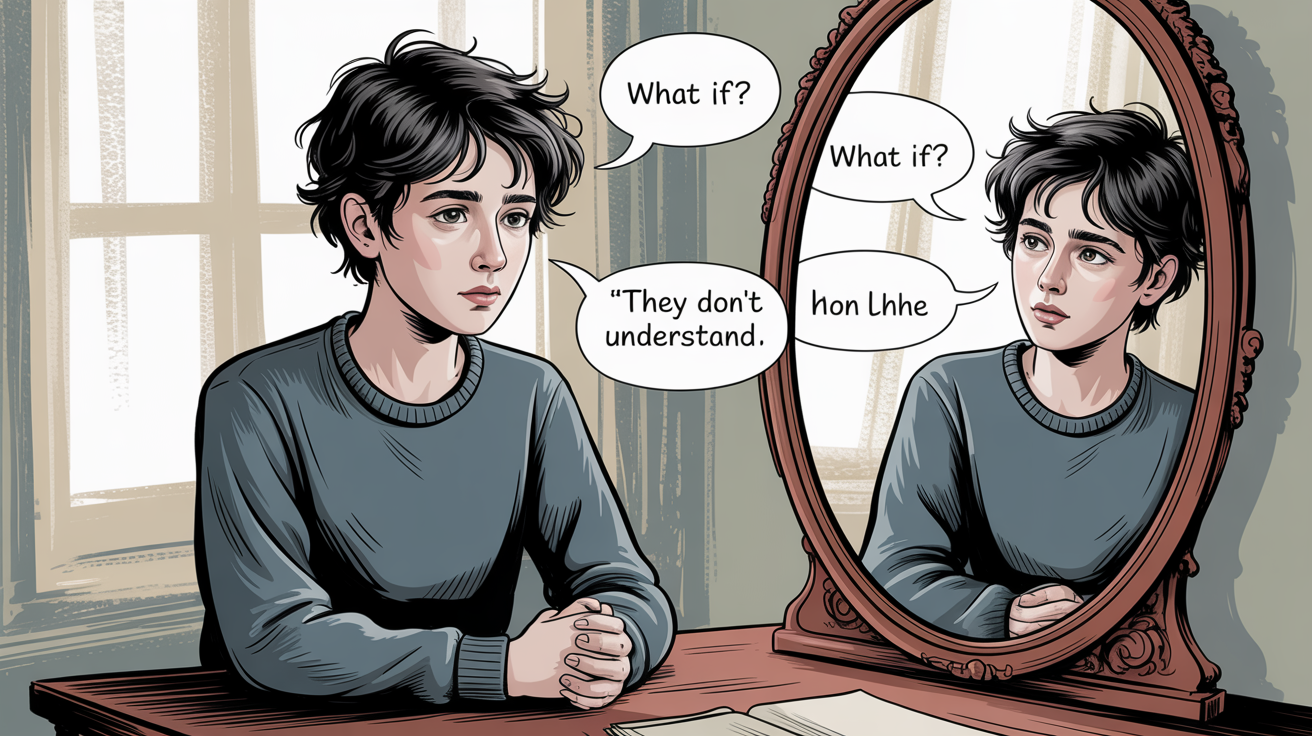
Communication is powerful, but it’s not always perfect. Many times, important messages get lost, misunderstood, or completely ignored because of different barriers to communication. These barriers can be psychological, like personal emotions or perceptions, or physical, like noise and technical problems. In this blog, we’ll explore the major types of barriers to communication with easy examples — and why feedback is essential for making communication successful.
Types of Barriers to Communication
🧠 Psychological Barriers
Psychological barriers arise from the mindsets, emotions, and expectations of the people involved in the communication.
Contents
👀 1. Perception
“The effectiveness of communication is limited by the receiver’s range of perception. People often perceive only what they expect and understand.”
In simple words:
Everyone sees the world through their own filters.
If someone already has certain fixed beliefs or expectations, they might misunderstand or ignore parts of your message — even if you communicate it perfectly!
Example:
If you believe a subject is boring, no matter how exciting the speaker makes it, you might still find it dull!
🕶️ Perception: Like Wearing Different Glasses!
Imagine that everyone wears invisible glasses —
and these glasses are made from their past experiences, beliefs, emotions, and expectations.
When a message comes in, people don’t see it exactly as it is —
they see it through the color and shape of their own glasses.
- If your glasses are clear and clean, you understand the message accurately.
- If your glasses are colored or scratched, the message looks different — it gets distorted or changed without you even realizing it!
✨Simple Example:
- A person who had a bad experience with teamwork in the past might see every new team project negatively — even if the new project is positive and exciting!
👥 2. Audience Interpretation
Communication must capture and relate to the receiver’s needs to be effective.
If your audience doesn’t feel the message speaks or matches their interests, they may lose attention quickly.
Example:
A health ad targeted at teenagers must use their style, slang, and interests — otherwise, it will just be ignored.
❤️ 3. Emotional Preference or Rejection
“Communication makes a demand on the recipient, based on their emotional preference or rejection.”
This means how the receiver feels about the sender or the message deeply impacts communication.
If they like or trust the sender, they are more open and accepting of the message.
If they dislike or distrust the sender, they may reject or misinterpret the message, even if it’s true or helpful.
Example:
Advice from a friend you trust will hit differently than the same advice coming from someone you don’t like.
🏢 Physical Barriers
Physical barriers are external factors that make the delivery or reception of the message difficult.
🔊 1. Noises or Distortions
“The source encodes a message and sends it through a channel, but noise or distortion can disrupt the process.”
Physical noise can literally block the message from reaching the receiver.
Example:
Trying to have a serious conversation in a crowded, noisy cafe/ restaurant — you may miss half the words!
📡 2. Medium of Transmission
Sometimes the tool or technology used to send the message can itself become a barrier.
If the receiver can’t access or properly understand the medium, communication fails.
Example:
- A podcast played for someone who can’t hear — ineffective.
- Complex graphs shown without explanation to a non-technical audience — confusing!
🔄 Importance of Feedback in Communication
Communication is a dynamic, two-way process where feedback plays a critical role.
- Feedback tells the sender whether the message was understood correctly.
- It allows the sender to adjust, clarify, or repeat the message if needed.
- It ensures that the desired action or understanding is achieved.
Without feedback, communication would be like talking into a void — you would never know if your message made a difference!
Final Thought
Understanding barriers and the power of feedback makes you a much stronger communicator.
Whether you’re speaking, writing, or presenting — always remember:
👉 Break down psychological and physical barriers.
👉 Seek and value feedback.
👉 Communication is a living process — it grows when both sides stay connected!
🎯 Quick Summary
| Type of Barrier | Examples |
| Psychological | Perception filters, emotional bias, loss of attention |
| Physical | Noise, wrong choice or inaccessible medium/ channel |
| Essential for Success Communication | Feedback loop |
Let’s Break the Barriers!
Have you ever faced a situation where a simple message got misunderstood because of perception, noise, or emotions? Share your experience in the comments below! 💬 Communication is powerful, but it’s not always perfect. Many times, important messages get lost or misunderstood because of barriers. If you’re new to the topic, check out our guide on What is Communication to understand the basics first.
Loved this guide? Don’t forget to share it with your friends and classmates who are learning communication too!